Description
유효한값(1)을 가지는 4방향으로 연속된 최대 면적을 구하는 문제입니다.
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid. An island is a group of 1's (representing land) connected 4-directionally (horizontal or vertical.) You may assume all four edges of the grid are surrounded by water.
The area of an island is the number of cells with a value 1 in the island.
Return the maximum area of an island in grid. If there is no island, return 0.
Example 1:
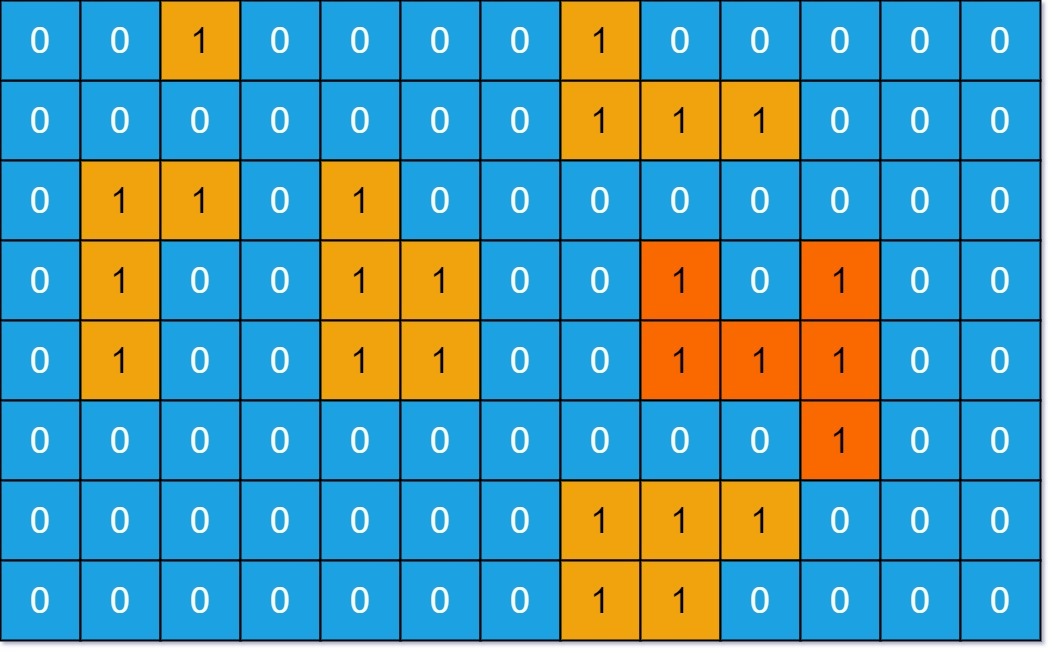
Input: grid = [[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
Output: 6
Explanation: The answer is not 11, because the island must be connected 4-directionally.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]]
Output: 0
Constraints:
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 50
- grid[i][j] is either 0 or 1.
Solution 1. DFS(Depth-First Search) - 깊이 우선 탐색
private final int[][] DIRECTIONS = new int[][]{{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1}};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int max = 0;
boolean[][] isVisited = new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(!isVisited[i][j]){
max = Math.max(max,dfs(grid,isVisited,i,j));
}
}
}
return max;
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid,boolean[][] isVisited, int r, int c){
if(r < 0 || r >= grid.length || c < 0 || c >=grid[0].length || isVisited[r][c] )return 0;
isVisited[r][c] = true; //방문 기록
int area = 0;
if(grid[r][c] == 1) { //섬이면 주변 섬 스캔 rercusive call
area++;
for(int[] d : DIRECTIONS){ // 시계방향 전파
area += dfs(grid,isVisited,r+d[0],c+d[1]);
}
}
return area;
}
첫번째 방법은 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)로 찾아 나가는 방법입니다. 특정 지점에서 시작하여 dfs() 함수 재귀호출을 통해 유효한 섬(1)로 확장해나가며 섬의 크기를 반환 받고 이 중 가장 큰 값이 정답입니다. 다음 섬을 탐색할때 이미 탐색했던 배열은 체크하지 않기 위해 isVisited 배열을 별도로 두고 기록을 남겨둡니다.
Solution 2. BFS(Breadth-First Search) - 너비 우선 탐색
private final int[][] DIRECTIONS = new int[][]{{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1}};
public int maxAreaOfIsland2(int[][] grid) {
int max = 0;
boolean[][] isVisited = new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == 1 && !isVisited[i][j]){
max = Math.max(max,bfs(grid,isVisited,i,j));
}
}
}
return max;
}
private int bfs(int[][] grid,boolean[][] isVisited, int r, int c){
int area = 0;
// 시작노드 queue 삽입 & 방문 기록
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[]{r, c});
isVisited[r][c] = true;
// queue 반복 - 시작지점의 유효한 인접노드 queue 에 넣고 순서대로 반복
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = q.poll(); // 시작지점 > 인접한노드 전체 > 인접한 노드의 인접노드 순으로 쌓임
area++;
for (int[] d: DIRECTIONS) { //인접 노드 반복 체크
int x = curr[0] + d[0];
int y = curr[1] + d[1];
if (x < 0 || x >= grid.length || y< 0 || y >= grid[0].length || isVisited[x][y] || grid[x][y] != 1){
continue;
}else { // 인접 노드가 유효한 노드 일 경우 큐에 넣어주고 순서대로 반복, 인접노드의 다음 뎁스의 인접노드가 큐에 들어가지만 먼저 들어간 낮은 깊이 부터 실행된다.
q.offer(new int[]{x, y});
isVisited[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
return area;
}
두번째 방법은 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)을 사용하였습니다. 접근방법은 유사하게 행렬로 반복하며 최초 유효한 값을 가지는 배열(1)을 만났을 때 너비우선 탐색으로 bfs() 메서드에서 area 값을 찾아내어 반환받습니다. 깊이우선탐색(DFS)와 다르게 재귀호출로 값을 받는 것이 아닌 queue를 이용하여 동일 깊이의 인접한 노드들부터 차례차례 찾아내어 반환하는 점이 다릅니다.
Reference
Max Area of Island - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
'알고리즘 > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node - 문제풀이 (0) | 2022.01.13 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] 617. Merge Two Binary Trees - 문제풀이 (0) | 2022.01.12 |
| [LeetCode] 733. Flood Fill - 문제풀이 (0) | 2022.01.12 |
| [LeetCode] 567. Permutation in String - 문제풀이 (0) | 2022.01.11 |
| [LeetCode] 3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters -문제풀이 (0) | 2022.01.11 |
